The Settings Screen
You can set the working settings to suite your needs. This section explains about the settings
that appear in the Settings Screen and about a few settings that don’t.
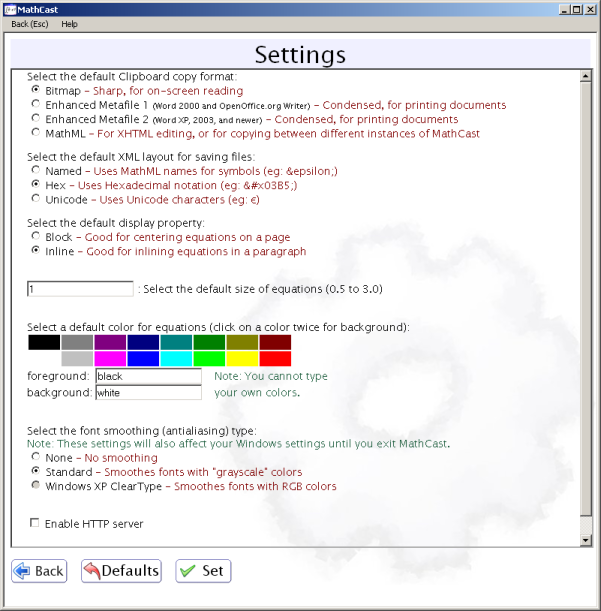
After you select your settings, press “Set” to apply and save them.
Clipboard Copy Format
MathCast uses an image format to copy equations. There are 2 formats: Bitmap copy and Enhanced
Metafile copy. MathCast uses a “screen-copy”, what’s rendered on the screen is what is copied
to the clipboard.
Use the Bitmap copy, if you know the document is for on-screen reading or for a webpage.
With Bitmap copy the equation would look exactly as it does in the Edit Screen. Bitmap
copy however is not sharp enough for high quality printing.
Use the Enhanced Metafile copy if you want to create a document with sharp equations for
printing. In order to get more detail, MathCast first enlarges an equation, then copies it.
If an equation is too large and doesn't fit in MathCast's window, you’ll have to maximize
the window, in order to have it copy correctly. There are two types of copy:
the first pastes in nicely in Word 2000, WordPad, and OpenOffice.org Writer, while the second
pastes better in Word XP, Word 2003 and newer.
Use MathML copy if you want to copy the MathML generated by MathCast. This copy format must be
selected in order to copy equations between different instances of MathCast on the same computer.
XML Layout
MathCast gives you some control over the output of the MathML it produces.
-
Named – MathML characters are replaced by their name (for example the character
“π” is replaced with “π”).
-
Hexadecimal – MathML characters are replaced with XML standard hexadecimal
notation (for example the character “π” is replaced with “π”).
-
Unicode – MathML characters are left as Unicode characters
(“π” remains “π”).
If Unicode is selected, MathCast will save files with "UTF-16" encoding type, otherwise it will
save in ASCII format.
Display Types
MathCast supports two display types for equations: “Block” and “Inline”.
Textbooks usually use “Block” when centering equations, like this:
The Schrodinger equation states that:
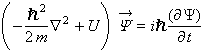
Where the m stands for…
And they use “Inline” when writing an equation in the middle of a sentence, like this:
The Schrodinger equation, 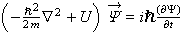 ,
is one of the fundamental equations in Quantum Physics…
,
is one of the fundamental equations in Quantum Physics…
Notice the differences in the parenthesis size and in the size of some of the characters.
Math Styles
You can set the default size, color and background color for your equations.
At the current version, MathCast supports only the basic colors.
Font Smoothing Type
You can set the level of smoothing or antialiasing for equations. This setting will also affect
the default font smoothing setting for all other running applications, until MathCast is closed.
- None: The equations will be drawn with only one color.
- Standard: The equations will be smoothed with "grayscale" colors.
- ClearType: The equations will be smoothed with RGB colors. This option can only be selected in Windows XP or newer.
Equations with smoothing, will take slightly more space on the hard drive, when exported to picture files.
Enable HTTP Server
MathCast allows people to work together on equation lists over a network and across the Internet.
This feature is described more in detail in the section labeled
Downloading Equation Lists.
To enable this feature check the checkbox, then choose the port number for incomming connections, click on "set", and restart MathCast for the settings to take effect.
Additional Settings
These options can be set by editing with notepad the “MathCast 0.9 Settings.xml” file.
The file is located in "C:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Application Data\MathCast" on Windows 2000 and XP.
You can customize the colors MathCast uses to draw the Edit Screen by changing their hexadecimal color codes:
- tableColor - the blue table where all the equations are drawn into.
- selectionBoxColor - the pink box that surrounds the selected equation.


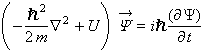
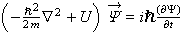 ,
is one of the fundamental equations in Quantum Physics…
,
is one of the fundamental equations in Quantum Physics…